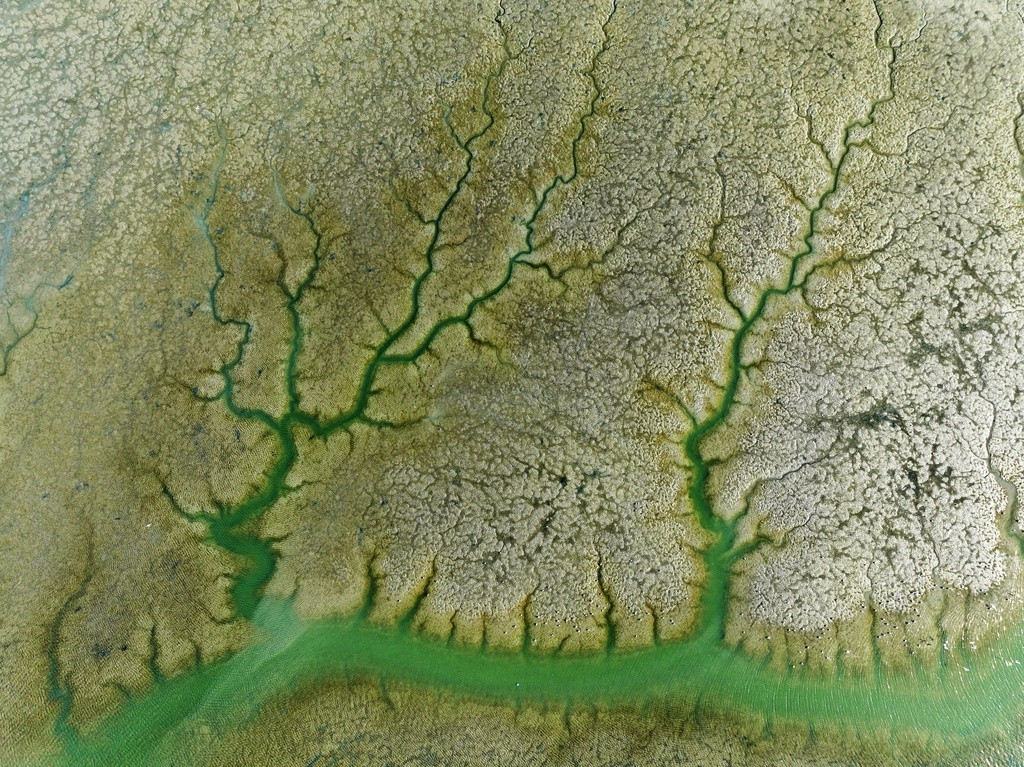
** turbulence **
** turbulence ** refers to the state of a fluid where there is a rapid and irregular flow of particles. This phenomenon can be observed in various natural and artificial settings, such as in the movement of water in rivers, the flow of air in the atmosphere, or even in the behavior of gases in combustion engines. The study of turbulence is crucial in many fields, including meteorology, engineering, and physics, as it helps in understanding and predicting complex fluid dynamics.
When ** turbulence ** occurs, the flow of the fluid becomes highly irregular, with fluctuations in velocity and pressure. This chaotic behavior can lead to the formation of eddies and vortices, which further complicate the motion of the fluid. These eddies can vary in size, from large-scale structures that span the entire flow field to smaller, more localized ones. The interaction between these structures is what gives turbulence its unpredictable nature.
Understanding the mechanisms behind ** turbulence ** has been a challenging task for scientists and engineers. Despite significant advancements in computational fluid dynamics and experimental techniques, a complete theoretical framework to describe turbulence is still elusive. One of the key aspects of turbulence research is the study of its statistical properties, such as the distribution of energy across different scales of motion. This has led to the development of models like the Kolmogorov theory, which provides a scaling law for the energy spectrum in isotropic turbulence.
In practical applications, controlling and predicting ** turbulence ** is essential for optimizing the performance of various systems, such as aircraft wings, pipelines, and wind turbines. For instance, reducing turbulence in airplane wings can lead to decreased drag and improved fuel efficiency. Similarly, in the design of wind turbines, understanding turbulence helps in enhancing the stability and energy capture of the system. Furthermore, in the field of meteorology, predicting turbulent conditions in the atmosphere is vital for weather forecasting and aviation safety.
Another important aspect of ** turbulence ** is its role in mixing processes. In many natural and industrial systems, turbulence enhances the mixing of fluids, which is essential for processes like chemical reactions, heat transfer, and the dispersion of pollutants. The chaotic motion of turbulent flows ensures that substances are mixed more efficiently than in laminar flows, where the mixing is primarily driven by molecular diffusion.
In summary, ** turbulence ** is a complex and fascinating phenomenon that plays a significant role in various scientific and engineering disciplines. While we have made considerable progress in understanding its characteristics and behaviors, there is still much to learn. Continued research and advancements in computational and experimental techniques will undoubtedly shed more light on the mysteries of turbulence, enabling us to harness its potential and mitigate its challenges in real-world applications.
turbulence #fluiddynamics #chaoticher #complexsystems #eddyflows

雷军回应29元2个的不锈钢直饮杯销量超3倍卖爆:用Ultra的闪电黄制作的
极目新闻

美以反对的埃及版加沙重建计划 到底说了点啥?一文解析→
央视新闻客户端

中国人民银行行长:今年将择机降准降息
新华社

拥有全部41个工业大类!《人民日报》整版推介“好客山东 好品山东”
人民日报

两会日程预告|3月5日:十四届全国人大三次会议上午9时开幕
新华社

专家详解:为何对自美进口相关光纤产品发起反规避调查?
新华社

政府工作报告丨2025年政府工作十大任务
新华社

民进党当局禁止与大陆理工名校交流合作 国台办:夜郎自大,阻碍交流
央视新闻客户端

首场“部长通道”集中采访活动明天上午举行
央视新闻客户端
山东大学第一幼儿园开展AI体验活动
海报新闻